There are many different types of electric motors, this is a graph that shows the different kinds:
| Self-Commutated | Externally Commutated | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical- Commutator Motors | Electronic- Commutator (EC) Motors | Asynchronous Machines | Synchronous Machines | |
| AC | DC | AC | AC | |
| * Universal motor (AC commutator series motoror AC/DC motor) * Repulsion motor | Electrically excited DC motor: * Separately excited * Series * Shunt * Compound PM DC motor | With PM rotor: * BLDC motor With ferromagnetic rotor: * SRM | Three-phase motors: * SCIM * WRIM AC motors: * Capacitor * Resistance * Split * Shaded-pole | Three-phase motors: * WRSM * PMSM or BLAC motor - IPMSM - SPMSM * Hybrid AC motors: * Permanent-split capacitor * Hysteresis * Stepper * SyRM * SyRM-PM hybrid |
| Simple electronics | Rectifier, linear transistor(s) or DC chopper | More elaborate electronics | Most elaborate electronics (VFD), when provided | |
Rotor: In an electric motor the moving part is the rotor which turns the shaft to deliver the mechanical power. The rotor usually has conductors laid into it which carry currents that interact with the magnetic field of the stator to generate the forces that turn the shaft. This is an example of a rotor and.
Stator:The stationary part is the stator, usually has either windings or permanent magnets. The stator is the stationary part of the motor’s electromagnetic circuit. The stator core is made up of many thin metal sheets, called laminations. Laminations are used to reduce energy loses that would result if a solid core were used.
Windings: Windings are wires that are laid in coils, usually wrapped around a laminated soft iron magnetic core so as to form magnetic poles when energized with current.
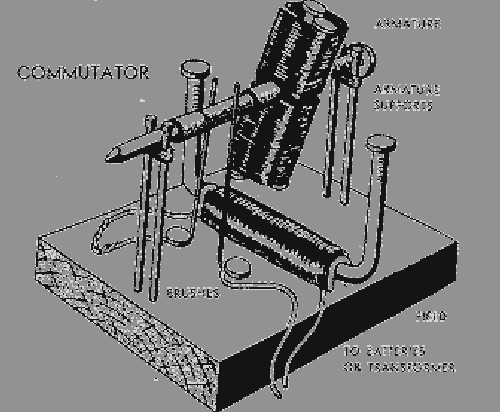
Commutator: A commutator is a mechanism used to switch the input of certain AC and DC machines consisting of slip ring segments insulated from each other and from the electric motor's shaft. The motor's armature current is supplied through the stationary brushes in contact with the revolving commutator, which causes required current reversal and applies power to the machine in an optimal manner as the rotor rotates from pole to pole. This diagram shows how a commutator operates:
Source: http://www.seaperch.org/electric_motors